A brick bond is a pattern in which the bricks are laid, this applies to both brick walls and brick paving for courtyards and paths, as well as for concrete blocks and other types of masonry wall construction.
To position the bricks and improve the appearance of the wall, mortar is used in between the bricks to make joints.
Here we will learn about brick bonds, types of brick bond & precautions to be taken in brick masonry work.
Introduction to brick bonds:
Bricks can be placed in various ways to provide strength, stability and decoration.
The way bricks are laid out is known as a bond and specific bond patterns develop over time.
The bricks are laid to act as a unit, arranging them in such a way that they are rested on top of each other and break the continuity of the vertical joints.
Various arrangements are practised for laying bricks.
Purpose of brick bonds:
- Bricks or stones are held together due to bonding.
- Bonds can cause brickwork to form a single unit.
- The bond forms a rigid wall structure.
- It increases the brief strength of masonry.
- It evenly distributes the load over a large area of the wall.
- Also, provides vertical joints in two successive layers of brick in a staggered manner.
Types of brick bonds:
1.Stretcher bond:
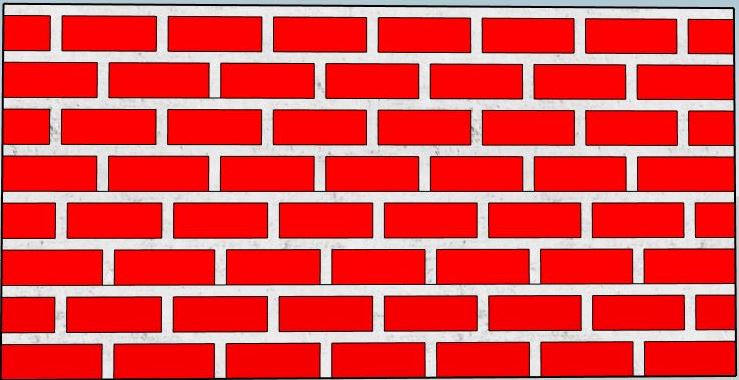
In stretcher of bond, all bricks are laid along their length in the direction of the wall.
This pattern is only used for walls with a thickness of half a brick i.e. 9 cm.
2.Header bond:
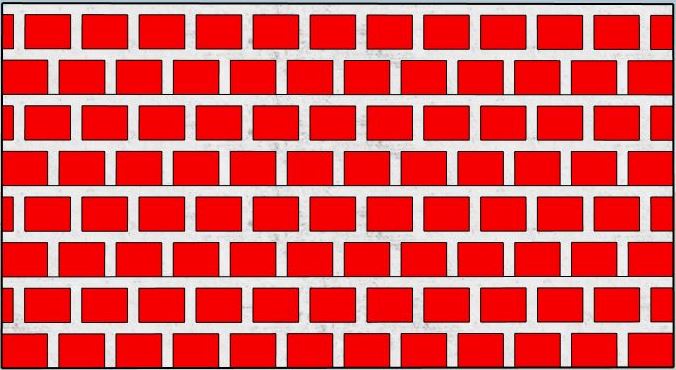
In header bond all the bricks are placed towards the face of the wall with their ends.
This type of arrangement is suitable for walls that are one brick thick, it is suitable for the walls of lightly loaded load-bearing structures.
3.English Bond:
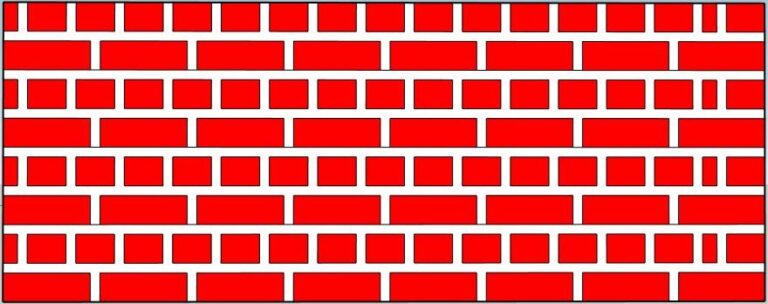
English bond is the most common and popular brick bonds used for wall thicknesses of 2 cm and more.
It has equal headers and stretchers in the wall arranged in header and stretcher elective courses.
The following points need to be consider while manufacturing english bond as follows:
- A queen should be provided close after the queen header.
- A header course should not start closer to the queen.
4.Flemish Bond:
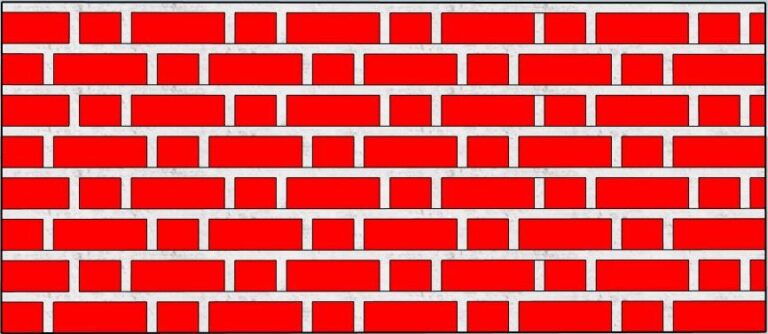
In this arrangement of flemish bonds, each course has optional headers and stretchers.
Each elective course begins with a header in the corner.
Types of Flemish Bonds:
A) Single Flemish Bond:
The combination of english bond and flemish bond results in a new type of bond called a single flemish bond.
B) Double Flemish Bond:
It is a specific type of flemish bond in which the same form in each course can be seen in the front face and the back face.
In short, the appearance of the wall on facing and supporting is the same in each course.
5.Garden wall Bond:

This type of bond is particularly used for building the garden or boundary wall.
In this bond, the height of the wall should not exceed 2 meters and the thickness of the wall is one brick thick.
Garden wall Flemish bond, Garden wall English bond & Garden wall monk bond are types of garden wall bonds.
6.Ranking Brick Bond:

When brick bonds in which bricks are placed on inclination in the direction of the wall called a ranking bond, this type of bond is used in a thick wall.
The longitudinal stability of the wall is higher in the case of ranking bonds therefore in such a bond is provided in the thicker wall of the english bond, the longitudinal stability is increased.
Herringbone bond & Diagonal bond are types of racking bonds.
Also read: Difference between English Bond and Flemish bond
Bricklaying patterns should fulfil the following points:
- All bricks should be of the same size and shape.
- The use of brick and stone should be discouraged.
- The arrangement of bricks should be uniform.
- The vertical joint of elective courses must be in a row.
important precautions considered in brickwork:
1. The bricks should be well burnt, reddish in colour, sound proof, hard and should have uniform shape and size.
2. Bricks should be as per the specifications.
3. Bricks should be soaked in the winter before using them into the masonry work.
4. Use of brickbats should not be more.
5. Brick masonry must contain brick bonds to transfer the load uniformly.
6. The bricks should be neatly and properly laid on the mortar.
7. The frog should be on the top surface.
8. Suitable brick bonds must be selected.
9. The brick masonry work should be done improper bond.
10. The brickwork should be perfectly in level.
11. Holdfast for doors should be properly cast in masonry work.
12. The brickwork used must actually be in plumb.
13. The motor used should be as per specification and fresh.
14. Construction joints should be provided after every 30 m to 50 m length of the wall.
Also read: Standard Brick Size & Bond Beam
Conclusion:
Bonds in brick masonry are developed by filling mortar between the layers of various types of bricks when they are placed adjacent to each other in layers.
The commonly used materials for bonding in brick masonry are cement mortar, lime mortar and clay mortar.

Related Posts
Rock Quality Designation(RQD): Building Strong Foundations
Spread Footing
Masonry Cement
Plain Cement Concrete
Concrete Efflorescence
Concrete Pile
Stepped Footing
Fineness Modulus of Coarse Aggregates
Difference between Condo and Apartment