Geotextile is a strong synthetic fabric that is used in construction projects such as highways or dam that have the ability to separate, filter, reinforce, protect, or drain.
In the case of the black mulch process, farmers need to remove the plastic but geotextile degrades over time.
In addition, there are other forms of geotextiles in which the major raw materials will be polyester, polyethylene, polypropylene, etc.
Here we will learn about geotextile, types of geotextiles, advantages and disadvantages of geotextiles.
Introduction to Geotextile:
Geotextile is basically a plastic material that has starch in major concentration and makes geotextile biodegradable.
These geotextiles are biologically and chemically inert, making them the least susceptible to bio-degradation which will eventually make them more durable.
These less biodegradable geotextiles are extensively used in agricultural industries, pharmaceutical industries and civil industries due to their high tensile strength.
Types of Geotextile:
Woven Geotextile Fabric:
They are normally found geotextiles made by adopting techniques that are similar to those of normal clothing.
They have the characteristic existence of two sets of parallel threads or yarns.
The yarn that runs parallel is called the warp and one perpendicular is called the weft.
Non-woven geotextile:
Nonwoven geotextiles are manufactured from steady filament yarn or short-staple fibre.
Fibres are bonded using thermal, chemical, mechanical or combination of techniques.
The thickness of the ground fibers obtained by mechanical interlocking or chemical or thermal bonding is 0.5–1 mm.
While chemically bonded nonwoven are relatively roughly on the order of 3 mm.
Knitted Geotextile:
Knitted geotextiles are collectively manufactured through interlocking a series of finished yarns.
All knitted geosynthetics are made by knitting methods in combination with another method of geosynthetics with weaving.
In addition, geonets, geogrids, geo-cells, geomembranes, geocomposites are the other types that have their own distinct characteristics used for special applications.
function of Geotextile :
Separation:
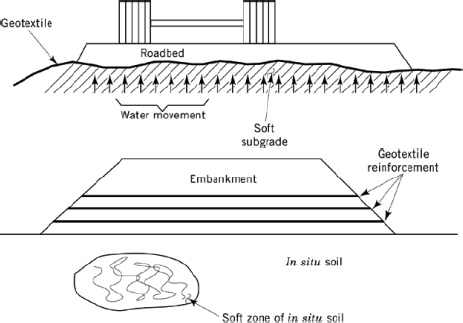
Separation work of geotextile is mainly used in the construction of roads.
Geotextile prevents the interception between two adjacent soils.
For example, separating fine subsoil soils from lower coarse aggregates preserves the drainage and strength characteristics of geotextile composite materials.
Filtration:
A balance of a geotextile to soil system that allows sufficient fluid flow in the plane of geotextile with limited soil loss.
Perforation and permeability are the most important properties of geotextiles with infiltration action.
Reinforcement:
The introduction of geotextiles into the soil will increase the tensile strength of the soil by the same amount of metal concrete.
Sealing:
A layer of nonwoven geotextile is saturated between existing and new asphalt layers.

Geotextile Installation Procedure:
- The surface is cleaned.
- Cracks are filled or repaired.
- Tack coat ranging from 1-1.351/m2 of residual asphalt is evenly applied.
- The paving fabric is laid with minimum wrinkles.
- Finally, a hot mix overlay is placed.
Advantages and disadvantages of geotextiles:
Merits:
- They are lighter in weight which makes it easier handling and laying on site.
- Transport and labor costs are less in real terms.
- Knitted geotextiles have a high tear strength.
Demerits:
- Installation of geotextile is critical and requires experienced contactors.
- These may delay seed germination, due to reduction in soil temperature.
- Geotextiles have maximum flow rate.
- Not suitable for areas that have foot traffic.
Also read: Difference between M Sand and River sand & Subgrade
uses of geotextileS:
It is used for sludge management.
For the improvement of mud-filled paths and trails that are used by cattle or light traffic, nonwoven fabric is used and twisted overlapping to include pipes or grit.
Playground Construction:
Large-scale geotextiles are used within the construction of castellon playgrounds and astroturf.
Caslon playgrounds are artificial grass surfaces that are constructed of light resistance polypropylene material with a 2.0 or 2.5 cm tall and non-perforated carboxylate latex backing pile.
Riverside and coal works:
Geotextile protects river banks from erosion caused by streams or lapping.
When used in combination with natural or artificial enclosures they act as a filter.
For the prevention of erosion, geotextiles can be used as woven or non-woven.
Railways Works:
Woven material or nonwoven is used to separate the soil from sub-soil without disrupting groundwater circulation where the ground is unstable.
Enabling individual layers with fabric prevents materials from sliding as a result of the shock and vibration of running trains.
Road work:
The basic principles of incorporating geotextile into the soil mass are similar to those used in the design of reinforced concrete by incorporating steel bars.
The fabric is used to impart tensile strength to the mass of the earth where shear stress is produced.
Also read: Soil Classification, Soil Liquefaction & Types of Sand
Conclusion:
Geotextile is an efficient and economic method of solving most of the geotechnical problems in roads.
The design engineer should be aware of the possible problems as well as using relatively new tools for solving them.





This information was very helpful to me.
thank you..
geotextile fabric stabilizes the ground by spreading loads over a larger area. By being lighter, less expensive, and thinner than layers of gravel, it makes financial and environmental sense to use this around your barn, stables and arenas.