A grit chamber consisting of sand, gravel, ash, or other elements.
The grit chamber is used to remove suspended debris like grit and coarse debris.
Grit chambers are used to safeguard industrial devices from abrasion and abnormal damage, reducing the frequency of digester.
In this article you’ll learn:
- Purpose of grit chamber.
- Types of grit chamber.
- Merits and Demerits of grit chamber.
- Lots more.
So, if you’re ready to go with a grit chamber, this article is for you.
Let’s dive right in.
What is a Grit Chamber?
A grit chamber is a long, narrow, or circular container in a primary sewage treatment plant.
It is used to lower the speed of the sewage flow in order to remove girt materials such as sand, ash and clinkers, eggshells, bone fragments, and other inorganic debris.
Purpose of Grit Chamber:
- The grit chamber removes inorganic grit, such as sand, gravel, and other mineral particles having a diameter of 0.15 to 0.20 mm or greater.
- Grit removal channels are designed to eliminate all particles having a specific gravity of at least 2.65, a diameter of at least 0.20 mm, and a settlement speed of at minimum 0.02 m/s.
- Some grit removal channels are designed to eliminate particles larger than 0.15 mm with a settling speed of 0.015 m / s.
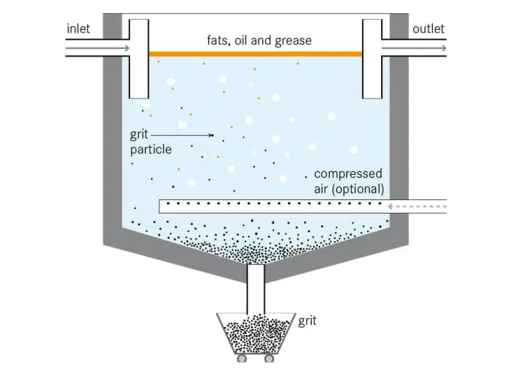
Types of Grit Chamber:
Horizontal Flow:
A long, narrow conduit is used in this sort of grit chamber.
In the plug flow model, effluent from this conduit runs with minimal mixing, which aids particle disposal.
The length to breadth proportion of the channel is raised to lessen the mix.
The inlet and outflow regions should have a minimum depth of approximately twice the maximum depth of 20 to 50 percent of the channel’s theoretical length.
The width of the duct is usually kept between 1 and 1.5 m, while the depth of flow is usually kept moderate.
A minimum of 0.3 m freeboard and 0.25 m grit space is provided.
Parallel two or more grit chambers are installed for large sewage treatment plants.
The chamber should be stopped after 30 to 60 seconds.
Aerated Grit Chamber:
Aerated grit chambers can simplify grit processing maintenance of equipment.
At maximum flow, it is built for a normal detention time of 3 minutes.
The 0.9 m deep grit hopper is located on one side of the tank under the air diffuser.
The diffusers are about 0.45 to 0.6 m below the surface.
The size of the removed particles is determined by the speed of the roller or movement.
The effluent is pumped into the grit chamber in the direction of the wheel.
The volume expansion due to air input must be considered in the design.
Vortex Girt Chamber:
Vortex grit chambers are used in smaller plants and take up less space than previous models.
To eliminate grit, the vertex flow pattern is employed.
Sewage enters vertically and exits vertically at the top or side.
If the grit particles remain in the chamber due to inertia, only the liquid which is not contaminated by grit will come out.
Rotating turbines help to separate organic matter from soot by maintaining a uniform speed.
By properly supplying wastewater to the chamber in a tangential direction, the centrifugal force on the grit particle can be maintained without a turbine.
Grit particles adopt a toroidal flow path due to propeller motion.
Working Principle of Grit Chamber:
Grit chambers can be effectively designed as sedimentation tanks.
Grit particles are considered to be separate particles that stabilize at different speeds.
The speed of stabilizing is determined by the size of the grit particles to be segregated, their specific gravity, and the viscosity of the effluent.
In circumstances where a large number of debris is likely to be carried in the sewage.
The grit to be cleaned should be at least 0.20 mm in size, and 0.10 to 0.15 mm in size.
The grit’s specific gravity can be as low as 2.4, however, 2.65 is utilized for design purposes.
Depending on the Reynolds number, the stabilization speed of different particles can be calculated using the correct equation.
Stroke’s Law:
Vs =g/18(Ss-18) d2/v
were,
Vs: Settling velocity
g: Acceleration due to gravity
d: Size of the particle
ν: Kinematic viscosity of sewage
Ss: Specific gravity of grit particle, dimensionless
For grit particles of specific gravity of 2.65 and liquid temperature at 10 degrees.
Transition law:
Vs=60.6(Ss-1) d 3T+70/100
Were,
T: temperature
The settling velocity of grit particles is in the range of 0.1 mm and 1mm.
Newton’s Law:
Vs=[3.3g(Ss-1) d]0.5
Advantages of Grit Chamber:
- To avoid friction and excessive stress when operating mechanical equipment.
- Reduce the cost of digester maintenance by reducing the frequency of cleaning due to grit accumulation.
- Heavy deposits in pipelines and channels should be avoided.
- For a wide flow range, they have standard extraction functionality.
- They are easy to use when it comes to adding chemicals, mixing, and pre-aeration and flocculation stages.
- The efficiency of the downstream division can be enhanced by initiating the pre-emission phase to identify septic problems while receiving sewage.
Disadvantages of Grit Chamber:
- They are more likely to produce toxic odours and toxic organic matter.
- Aeration system control and maintenance will influence various human resources.
- Compared to other girt removal technologies, they require higher energy resources.
Related Articles: Coarse Aggregates | Types of Aggregates | Caisson Foundation
Conclusion:
Grit chamber treatment technologies such as membrane systems as well as the growing need to maximize investment in equipment, and focus more on effective grit removal.
While both technologies claim 95% grit removal, there are significant differences in the size of these systems and how they remove grit.

Related Posts
Rock Quality Designation(RQD): Building Strong Foundations
Spread Footing
Masonry Cement
Plain Cement Concrete
Concrete Efflorescence
Concrete Pile
Stepped Footing
Fineness Modulus of Coarse Aggregates
Difference between Condo and Apartment