The reconnaissance survey is a detailed investigation of a whole area that could be used for a highway or airport.
The proper analysis of a site to determine its suitability for a planned civil and structural project is known as a reconnaissance survey.
In this article you’ll learn:
So, if you’re ready to go with a reconnaissance survey, this article is for you.
Let’s dive right in.
What is a Reconnaissance Survey?
A reconnaissance survey is an excellent technique to learn about the region you are about to work in.
It is useful for mapping subterranean resources, terrain, and vegetation for various projects.
Purpose of Reconnaissance Survey:
- An engineer or surveyor performs the reconnaissance survey, which involves topographical surveys, site management, and preliminary design estimated costs.
- This survey is the type of field survey used to gather preliminary information on the presence or absence of historic properties in a project area.
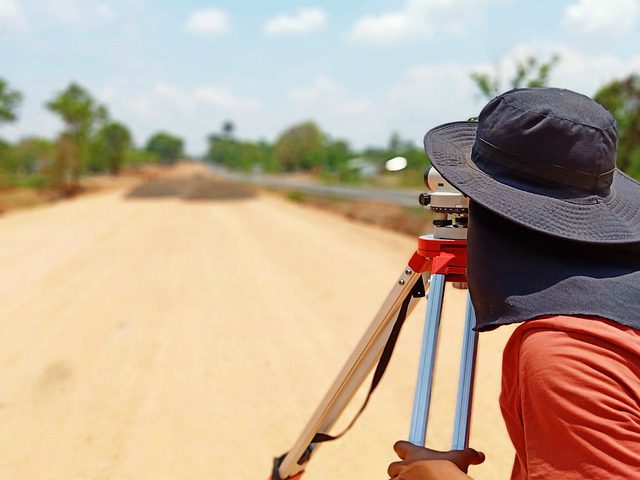

Design of Reconnaissance Survey:
During the reconnaissance survey, design and practical characteristics should be examined.
Take note that future operations may demand a more extensive road system.
The route specifications must be carefully examined. If none of these are available, the following can be utilized as a starting point.
Route components of the new highway along or over existing roads, railways, or pathways whenever feasible.
Drainage infrastructure should be reduced to a minimum by following slopes and streamlines. Keep the gradient well above the rising water line when pursuing a stream.
Build the road using contour lines to avoid the extra excavation work and choose a course that is as close to the source of resources as possible.
Choose a path that leads you as close to the source of the material as necessary, then construct the roadway along contour lines to save time and money.
Place the roadway on the warm side of mountains and valleys, as well as along the cliff wall, where the strata’s inclination tends to keep the road from slipping into the valley.
Roads should be disguised and shielded from enemy forces in advanced fighting zones. Engineering factors may sometimes conflict with this.
By eliminating rock construction and over-clearing, choose locations that save engineer resources.
Avoid abrupt turns and areas where you’ll need to cross a bridge.
Methods of Reconnaissance Survey:
Study of Survey Sheets and Maps:
The reconnaissance survey begins with the analysis of all relevant maps.
A number of cost-effective orientations are possible after studying the topographical features on the maps as follows:
- Alignment that considers all control points, is faster and less expensive and meets gradient and curvature parameters.
- The shape of the alignment.
- As much as possible, stay away from the swampy area, steep terrains, unsteady hill formations, and locations vulnerable to extreme climatic conditions, flooding, and drowning
- Need to interconnect important villages and towns.
- Problem-solving.
- The importance of preserving the ecosystem and maintaining ecological balance.
Aerial Reconnaissance Survey:
Aerial reconnaissance will provide you with a bird’s eye perspective of the alignments in the issue as well as the surrounding area.
It will help in levels of perceived that necessitate the rejection or modification of any of the alignments.
The aerial survey could be used to make the final choice regarding which alignments should be explored in-depth on the surface.
Ground Reconnaissance Survey:
Ground reconnaissance encompasses a broad assessment of the topography, which includes traveling or riding along probable routes and collecting all essential data for review.
In the case of hill parts, it could be a good idea to start the reconnaissance from a necessary point of view up to the summit.
If ground reconnaissance is not possible, an aerial approach should be used to eliminate any uncertainties.
For ground reconnaissance, compass, Abney level /altimeter, pedometer, aneroid barometer, clinometers, ghat tracer, and other equipment are frequently utilized.
Communication is helped with remote-control sets, which are particularly useful in hilly areas.
The use of the following instruments to obtain ground slopes, maximum gradients, the height of critical peaks or stream crossings, and the location of necessary points works as a check on the maps in use.
Reconnaissance Survey Reports:
Based on the facts acquired during the reconnaissance survey, a report should be drafted.
The report included all essential information obtained during the survey, as well as a map drawn to a scale of 1:50000 illustrating the different alignments examined, as well as an approximate cost estimate.
It should also highlight the benefits and drawbacks of the various options to aid in the choosing of one or several alignments for further inquiry and surveying.
Advantages of Reconnaissance Survey:
- It contributes to increasing the speed of the operation because it is completed before any other survey.
- It is cost-effective because the region has already been surveyed for roads.
- By minimizing the number of destinations, saves a lot of money and time.
- It facilitates a better understanding of the project area by setting forth guidelines in advance, hence reducing work-related errors.
- Due to a variety of criteria, it assures that reports are correct and dependable:
- The maps have been updated using the most recent information.
- The data was derived from topographic maps and aerial pictures.
Disadvantages of Reconnaissance Survey:
- The site may be larger than normal more time may be required to finish all components of the project, resulting in increased expenses.
- It is less successful than site-specific surveys since previously surveyed regions cannot be used for surveys, necessitating the survey and recording of new areas.
- It is difficult to follow and reproduce road materials and standards that are already in existence for a project, but only if the site can be discovered.
- The results of these surveys are unreliable because, no matter how thoroughly the region was previously examined on-site, there may have been changes that were not captured in the initial survey.
Application of Reconnaissance Survey:
Civil engineering: A group of engineers performs a reconnaissance survey, including maps of the route sites, lengths, soil categories, heights, river flows, transportation connections (roads and railways), cities, villages, and other communities in detail.
Hydrology: To get a good sense of the topography and surroundings of the planned hydro-meteorological measurement station.
Archaeology: To locate any archaeological sites and sociocultural resources around the recommended alignment.
Mining: It aids in determining whether or not a region has mineral resources.
Telecommunication: To get a sense of the current situation, possible service quality, such as accessibility, reliability, and speed, as well as the costs of acquiring these services from existing systems.
Related Articles: Theodolite Surveying | Compass Surveying | Chain Surveying | Plane Table Surveying
Conclusion:
The Reconnaissance Survey is the result of identifying and evaluating past resource levels in the community.
This paper identifies and evaluates past resource levels, as well as offers recommendations and suggestions for ensuring that the resources are recognized and preserved for ongoing and prospective users.





This has helped me a lot ,am doing studies at Malawi college of Forestly and Wildlife.In sourthen Africa.Malawi
well done and keep it up