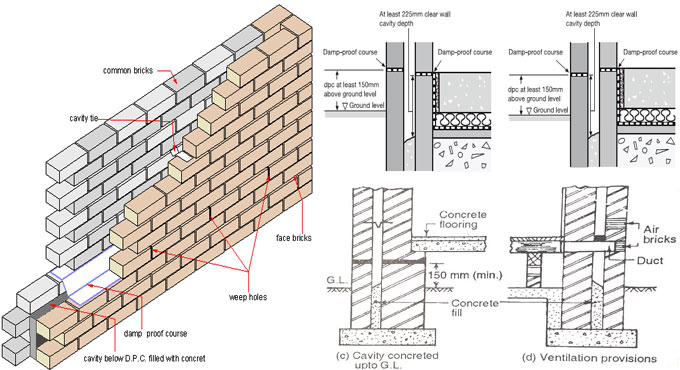
Cavity wall consist of two separate walls called leaves or skin with the cavity gap between these two different walls thus they are normally the outer walls of the building.
Here we will learn about cavity wall, purpose of cavity walls & where are cavity wall used?
Introduction to Cavity wall:
The cavity wall is a type of wall that has a hollow center.
For a load-bearing wall, the two leaves of cavity walls may be equal thickness whereas, for a non-load-bearing wall, the inner leaf may be thicker than the outer leaf.
Two separate walls on suitable interiors can be joined together by metal pins or bonding bricks.
Purpose of cavity wall:
- Cavity walls provides resistance to moisture penetration.
- They are also thermal energy efficiency.
- Also, fire resistance.
- It has several structural properties.
Advantages of Cavity Wall:
- In cavity walls, there is no possibility of moisture traveling from the outer wall to the internal wall.
- The air layer within the cavity walls is a non-conductor of heat and it reduces the transmission of heat from the outer face to the inner face.
- It acts as a damp barrier and reduces the cooling cost of the building.
- Maintains thickness of the prevailing wall.
- Minimum interrupt to install.
- Cavity walls give good insulation against sound, it makes the room soundproof.
- As the cavity or gap between the two leaves is filled with air which is a poor conductor of heat, the transmission of heat inside the room is reduced; it makes the room heatproof.
- The weathering is also significantly reduced.
- These types of walls are inexpensive and economical.
Disadvantages of cavity wall:
- Filling the cavity with insulation will always risk that moisture will have the ability to discover its solution to the inside, regardless of the insulation materials.
- There is also a possibility that the installation will cause unfinished air to come out of the pocket due to ‘cold spots’ on the inside walls, which attract condensation.
- Cavity insulation makes the outer brick leaf cool and subsequently wet, which strengthens the corrosion in wall ties and if the ties are to be modified, there is no passable way to refill the holes within the insulation.
- Thermal bridging issues.
- The thickness of the insulation is restricted by the width of the cavity walls.
- Throughout the cavity there is a vital number of buildings with mortar droplets on the ties, leading to damping of the moisture.
- Cavitation-settlement and saturation will promote cold bridging.
Uses of Cavity Wall:
Block construction:
Cavity walls has two half-brick thick leaves with a cavity between them.
The outer leaf in combination with the cavity acts as a barrier of moisture & the inner leaf supports the load from the floor and roof.
Insulation:
Cavity walls insulation is used to reduce heat loss, to fill the air space with materials that inhibit warmth transfer.
Wall Ties:
Wall ties make sure that the wall leaves are not removed from each other, effectively dividing the 2 leaves.
The normal distance of relationships has been determined in building regulations.
Cavity wall construction measures:
- The gap or cavity between two different walls or leaves should be uniform thickness at the height of the walls, it should not be less than 50 mm and not more than 75 mm.
- The two leaves may be similar in thickness when not subjected to heavy loads.
- The bricks are placed in cement mortar with a ratio of 1:4.
- In a load-bearing structure, mostly the inner leaf is thicker than the outer leaf.
- The outer and inner walls are joined together with the help of bond bricks or metal ties to achieve stability.
- Metal ties are also called cast iron cramps and wrought iron cramps, these ties are vibrated and must be placed at a vertical interval of 300 mm to increase the stability of two leaves.
Also read: Masonry Wall, Retaining Wall & Parapet Wall
Conclusion:
The cavity wall is usually an inner wall of the block or study work, a cavity that is usually untouched, and an outer wall of the face work, stone, or rendered blockwork.





This knowledge is quite useful. Amazing article.
Ideas that are both amazing and informative. Thank you for sharing the information.
thank you the information has been useful to me..i plan on creating a total soundproof hall