A deep foundation is a type of foundation that transfers building loads to the earth farther down than a shallow foundation does to a subsurface layer or a range of depths, the function of deep foundations is to transmit the weight of the building to the firm layers deep inside the ground.
Here we will learn about deep foundation, types of deep foundation & much more.
Introduction to Deep Foundation:
If depth of the foundation greater than its width, the foundation is called as deep foundation.
The depth to width ratio is larger than 4 to 5 in this foundation.
Deep foundations distribute the weight of the superstructure vertically rather than laterally as compared to shallow foundations.
This foundations are provided when the required loads from the superstructure cannot supported on shallow foundations.
Deep foundation can be selected in the following situations:
- The hard layer of soil at greater depth.
- Loading from the structure is concentrated on heavy soils.
- Offshore construction in marshy areas.
- Where a structure is susceptible to uneven settlements.
Type of Deep Foundation:
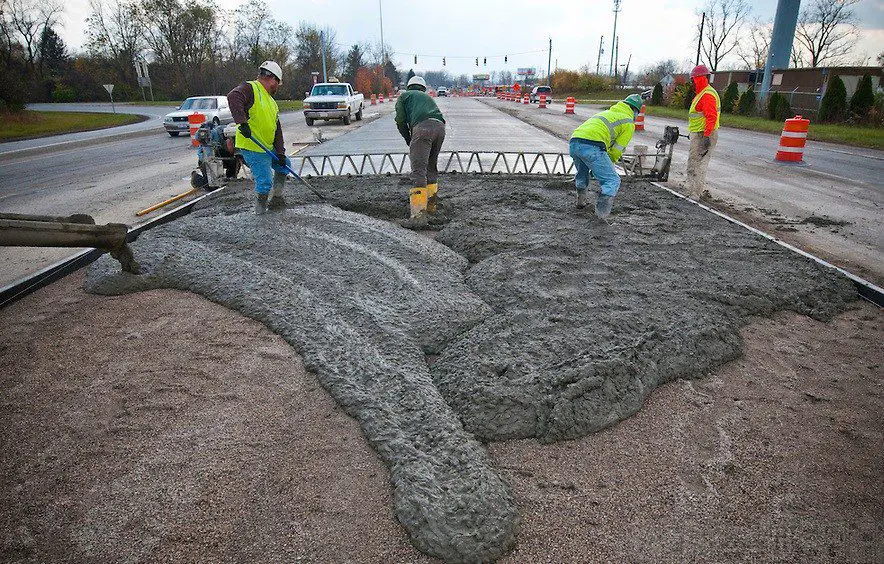
1.Pile Foundation:
The pile is defined as a tapered column capable of transferring structural loads to the underlying layers.
Uses of piles foundation:
- Piles are used to bear the vertical compressive load.
- Vertical piles are used to carry the vertical compressive load of superstructures such as bridges, buildings, etc.
- Piles are used for the foundation of a building to hold the load from the superstructure.
- Piles are also used to resist bending as well as horizontal forces.
- Use of piles to resist lateral loads in bridge and retaining wall structures.
2.Well Foundation:
Well Foundation is a watertight construction ideally manufactured from wooden, steel, R.C.C.
It is constructed in reference to excavation for the foundation of bridges, piers in rivers, dock structures, and so on.
Uses of the Well Foundation:
- This foundation is more suitable for underwater foundations.
- This foundation should be spread below or above the river bottom or the ocean floor to realize proper stability.
- These foundation has been built in connection with the excavation of the foundations of rivers and ponds, bridges, breakwater dock structures for the approach to rivers and ponds, ponds, deep houses, etc.
- Caisson is used as foundations for bridge piers, rivers, seas, lakes, breakers, and for sanctuaries in various coast, construction works.
- It can be used for home pumps that are subject to huge vertical as well as horizontal forces.
- It can be generally used for big and multi-story buildings and different structures.
3.Basement Foundation:
These are hollow substructures designed to operate below ground level or current storage space.
Structural design in an environmentally friendly way to resist the external environment and hydrostatic pressure is achieved by their functional requirements.
These types of foundations have been built in place of open excavations.
Uses of Basement Foundation:
- Daylight basements can be used for many purposes such as the garage, maintenance room, or living space.
- The buried part is used for storage, laundry rooms, hot water tanks, and HVAC.
- Daylight basement homes are usually taller than standard-basement homes include more viable dwelling areas in the deep foundation.
4.Hollow Box Foundation:
This foundation is hollow substructures designed to offer a semi-buoyant sub-structure, due to which the net loading on the soil is reduced to a lower intensity.
They can be designed to sink as caissons can be constructed in open excavations.
Uses of Hollow box foundation:
- This foundation is more environment friendly than pile foundation within the areas with very weak soils for large depths.
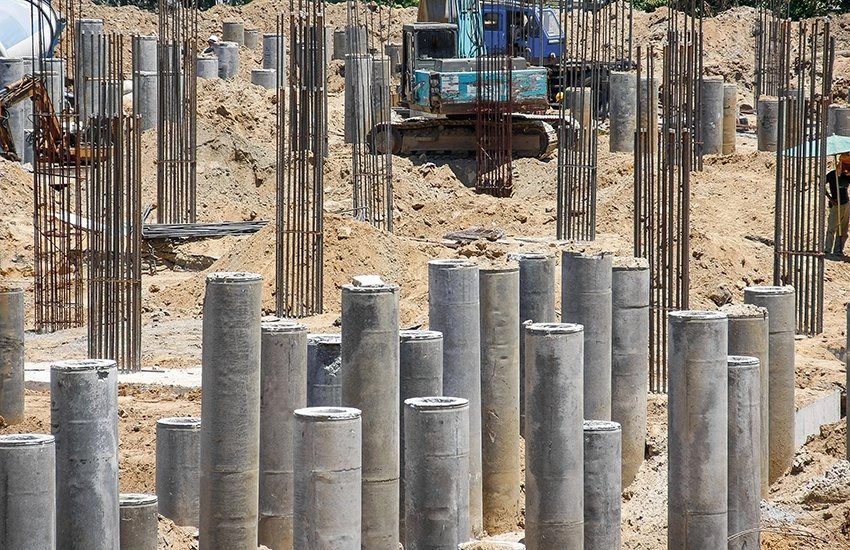
5.Drilling Shaft Foundation:
This foundation is constructed inside a deep excavation supported by a lining built in place, then filled with concrete or other prefabricated load-bearing components.
Uses of Drilling shaft foundation:
- It is largely used to help buildings with axial and lateral loads by digging cylindrical shafts into the ground and filling them with concrete.
6.Cylinder Foundation:
Cylinders are small single-celled casein.
Advantages of Deep Foundation:
- Piles can be prefabricated off-site which allows efficient installation on the site.
- The induced piles displace and compact the soil which will increase the bearing capacity of the pile.
- Piles will keep the facility safe and strong for many years.
- Increase overall productivity.
- A pile quickly damaged by driving through stones and boulders.
- Piles can be attacked by saltwater marine bits.
- A stack cannot be above ground level.
- It is very difficult to know the actual required length in advance.
- Vibrations are produced when the piles are driving which affects neighbouring structures.
Disadvantages of Deep Foundation:
- Piles can undergo corrosion.
- Daily inspection required.
- Skilled labor is required to fix the piles.
Also read: Pier and Beam Foundation, Floating Foundation & Mat Foundation
Conclusion:
Deep foundations are used to transfer structural loads to soil depth and when subjected to scour, it occurs as pile foundations and well foundations.





Thanks for this compilations I strongly appreciate this and I gained a lot reading and studying this . Cheers
That is fact’s
Thanks so much,I love all who have put their efforts to search for us this lovely information.
Am now a super engineer because of you
I really appreciate God bless you so muchooo