Whether building single-family houses, skyscrapers, or superstructures, selecting the best types of the foundation is critical.
The foundation serves two purposes: it transmits the weight of the load-bearing wall to the soil or bedrock underneath & keeps soil moisture out.
A foundation is a lower part of a structure that transfers its load to the soil (earth), the structure must distribute the load equally within tolerable limits.
In addition to the topography, geology, and paedology (the study of soil) of your building site, the foundation’s types are ideal for your structure and it will be determined by the size of your building and other considerations like types of construction.
In this post, we will discuss the foundation’s for building houses with examples.
We also provided all different types of foundations for homes and building construction with sketches to help highlight the benefits of each foundation.
What are the Different Types of Foundation?
The terrain beneath our feet might be made up of a variety of soils, stones, sediments, and other materials, geotechnical engineers must be aware of how these earthly elements affect the building and structural integrity.
Let’s briefly review the various foundation types used in building construction as follows:
1. Basement Foundation:
A hole at least eight feet deep is the first step in the construction of a basement foundation to make room for a subterranean drainage system.
Living room with floor space includes the ground level of the property.
The walls of the structural foundation will be constructed around the basement’s perimeter at the base of the concrete.
The additional living space is the apparent benefit of a basement foundation.
In fact, if homeowners choose to finish it, the square footage of the house can increase by two times, and the basement foundations are sturdy, fireproof, and weatherproof.
They are frequently found in colder regions, i.e., Midwest, Mid-Atlantic, and Northeast.
In order to avoid the house from moving during freeze and thaw cycles, the foundation must always be set underneath the frost line, they can get the same heating or cooling as other parts of the house.
The foundation with a daylight basement is the most expensive type of foundation.
It is built on a slope that opens to the sun on at least one side, the area formed by this type of foundation might appear cave-like due to a lack of natural light.
If you live in a flood-prone area, building a basement is not a good idea and if you live in a low-risk location, experts suggest installing appropriate equipment such as a sump pump.
The sunlight basement is completely buried by the ground on at least one side.
It can be a wonderful alternative to a complete basement foundation for homes constructed on a slope, even providing a separate entrance to the property.
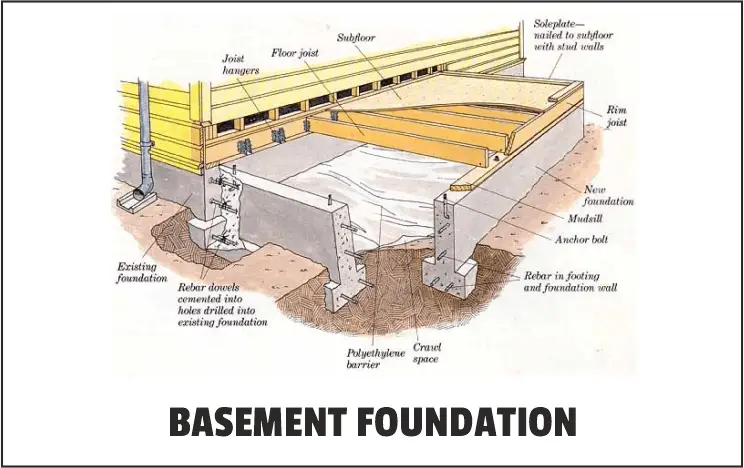
Types of Basement Foundation:
- Crawl Space Foundation.
- Full Basement Foundation.
- Daylight Basement Foundation.
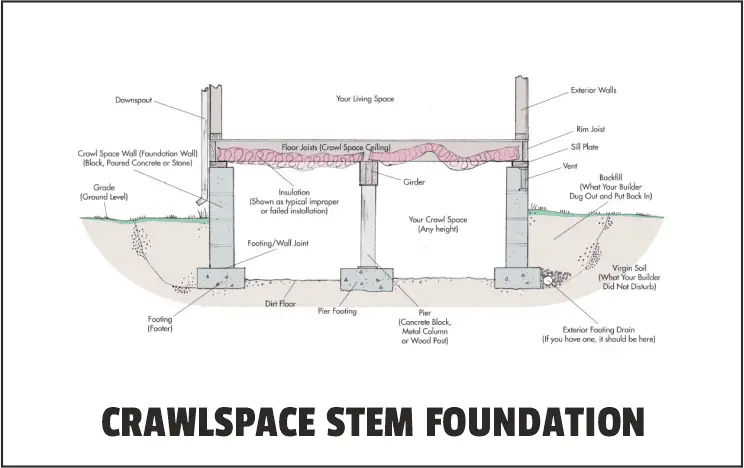
2. Crawlspace Stem Walls:
They construct a space that is exactly what it sounds like: a slightly elevated area beneath a house through which you can crawl, frequently with space for a furnace and other industrial equipment as well as storage.
Crawlspace foundations have the considerable potential to protect the home.
Raising the foundation shields the house’s walls from flooding and other environmental dangers.
This area has simple access to mechanical systems like wiring and plumbing.
A house’s entire structure is raised when the foundation is raised, which can produce a more aesthetically pleasing structure.
These types of foundation in building construction has less costly than excavating a whole basement.
Such foundations are more prevalent in warmer areas, such as California, Texas, the Northwest, and the South.
Additionally, they are a well-liked selection for architects designing homes in earthquake-prone regions.
Because they are elevated above the ground, crawlspace foundations are more resistant to termites, but the moisture that can collect beneath them makes them vulnerable to mould and mildew.
While basement foundations are more expensive than crawlspace foundations.
In order to keep them dry, homeowners must install vapour barriers, check for leaks near plumbing, and make sure that below-ground walls are free of cracks.
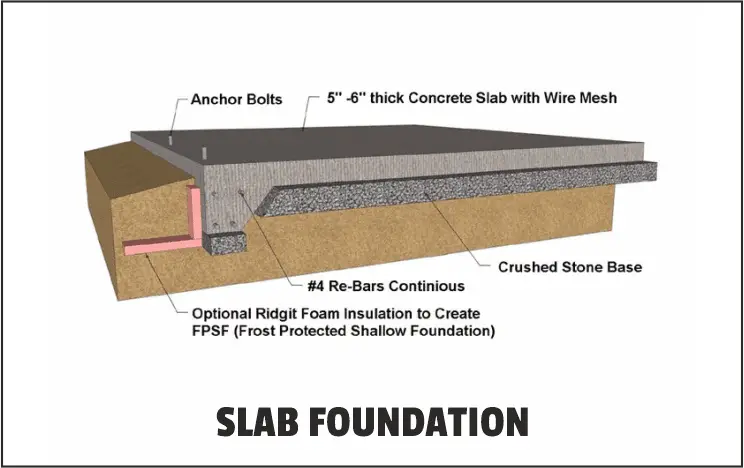
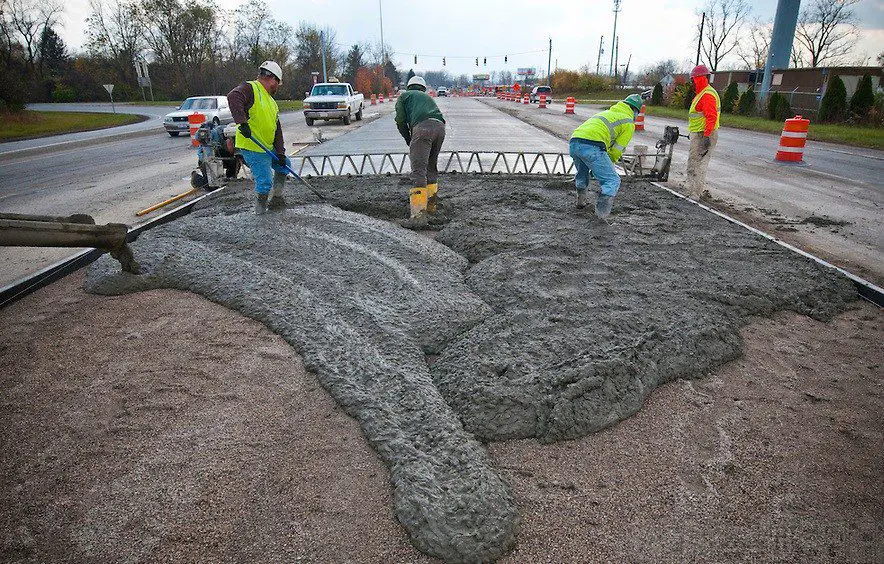
3. Slab Foundations:
Some other name for a slab foundation is a monolithic or mono slab foundation.
A monolithic foundation’s main benefit is that it is less expensive and takes less time to build. It is a level slab of concrete that is pumped in one piece and stays put.
In actuality, installation is a simple process in these types of foundation in building construction.
Around the slab’s perimeter, a two-foot-deep concrete-embedded beam with embedded wire mesh and steel reinforcement bars run.
Although structures built on a slab do not have crawl spaces, homeowners will not have to deal with the maintenance concerns.
A concrete slab that was cast on-site won’t have any weak spots that could fall apart over time and result in costly foundation repair issues.
However, they are rarely observed in icy environments: Concrete can crack and move as a result of the freezing and thawing of the earth.
Slab construction has the significant drawback of having sewer and drainage lines put in before the concrete is poured.
In the incident of a sewage or plumbing problem, you will need to cut into the slab to get to the pipes.
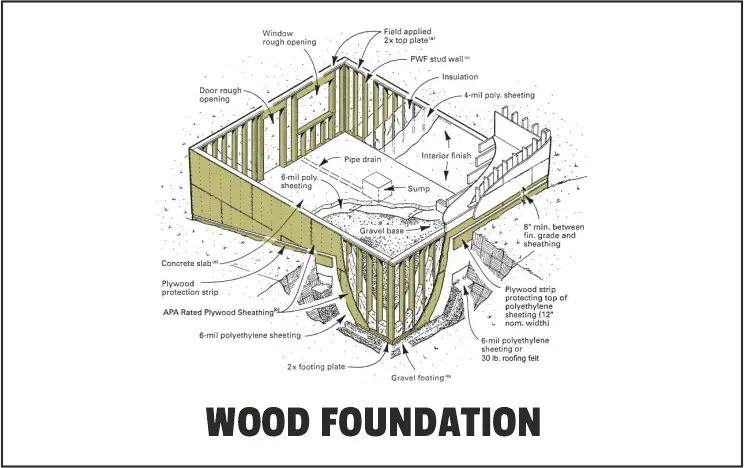
4. Wood Foundations:
Although wood might seem like an odd material for a foundation, it became more popular in the 1960s.
Preservative-treated wood that is easy to install and resistant to decay will be used by builders.
Since concrete pouring and labour-intensive masonry work are not necessary when building a wood foundation, it can be done more quickly and for less money.
Additionally, by insulating these foundations, builders can create a home that is less draughty and has a warmer crawlspace.
For those who are unsure about the durability of wood construction in the right setting, archaeologists have found beams made of Cyprus wood in Egyptian pyramids that are more than 6,000 years old.
Although some woods, such as cypress, redwood, and cedar, are resistant to insects and mildew they are expensive, the timber industry has developed methods of treating other lumber to give it comparable properties.
Although they may not last as long as concrete foundations, they can be used in totally dry soil.
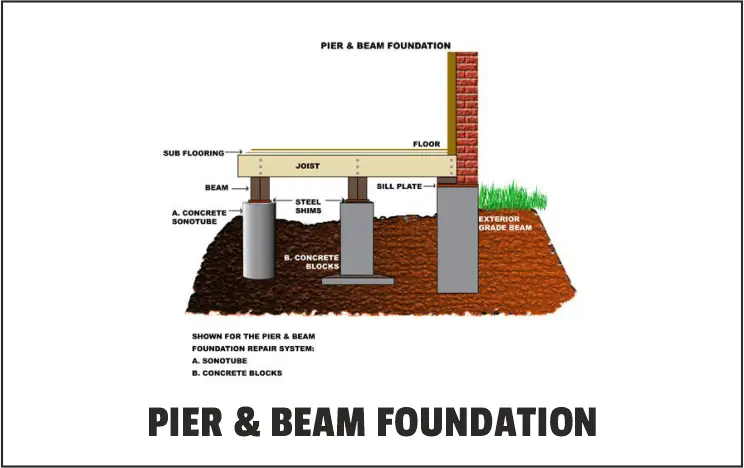
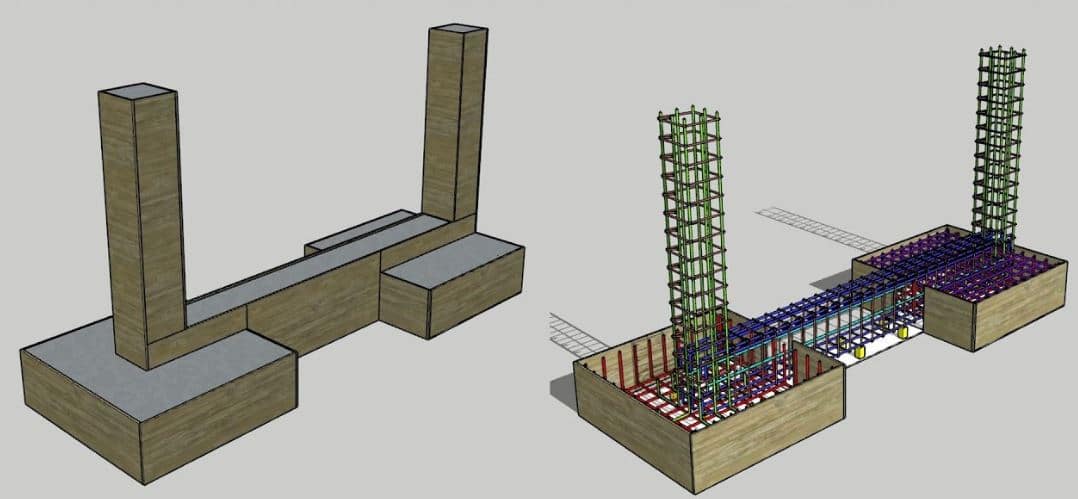
5. Pier and Beam Foundations:
In coastal areas, constructing a pier and beam foundation is the best way to keep a house above shifting, flooding, or eroding soil (also known as piers and piling or pier and post).
They are frequently discovered in areas that are vulnerable to hurricanes or severe flooding.
They must be carefully planned because they must support the house and shield it from moisture.
These enormous pillars, which are frequently over 15 yards long and fixed into the lowest strata of stone and earth, perform a similar function to an ocean pier.
Builders employ them with heavier structures because the pillars distribute the weight of the building across a wide region preventing the house from sinking.
A structural engineer will be required to supervise a project because soil analysis will be required to ensure that the structure is built in the proper circumstances.
Due to the need for heavy machinery when driving concrete piers, you should allow more time and money.
Different Types of Foundation based on Depth:
6. Deep Foundation:
Deep foundations are essential when constructing on sand or other soft soil that cannot sustain the load of the structure.
Instead, a foundation must be built deep below or perhaps underwater, where it may make touch with stronger strata of the soil.
Dams, piers, and bridges are a few examples.
They had to have kept the structural integrity while having submerged foundations.
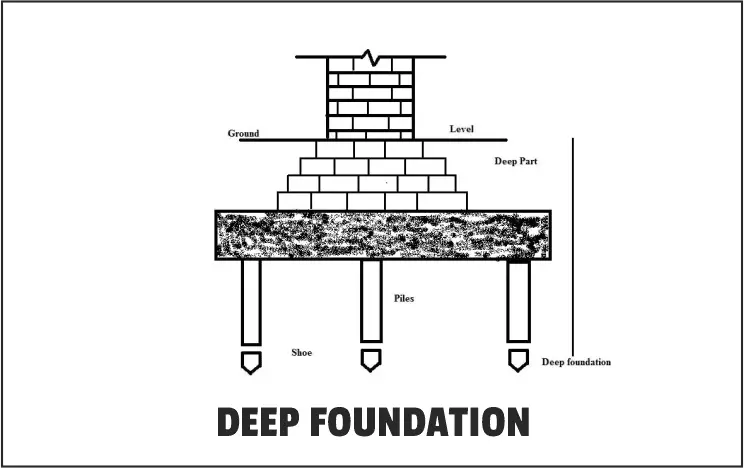
Types of Deep Foundation:
A deep foundation is more usually seen in bigger structures, although they can also be found in residences constructed on steep cliffs, above water, on the beach, or in other unusual sites.
They are constructed precisely where they comprehensive deep into the soil.
The primary examples are pile and caisson, each has certain subtypes that we have discussed.
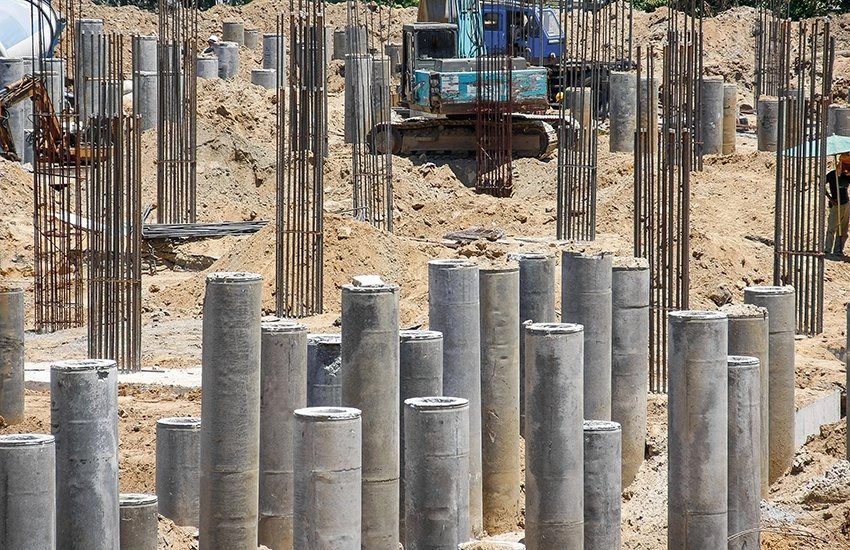
Pile Foundation:
The most common kind of deep foundation is the pile foundation.
Types of Pile Foundation:
The end-bearing piles and friction piles are the two forms of pile foundations, both involve drilling enormous, robust columns into the earth.
1. End-Bearing Piles:
End-bearing piles are driven as far into the surface as required to establish contact with the rock layer under the earth’s surface.
This permits the load to flow through the piling and into the bedrock, resulting in safe weight distribution.
2. Friction Piles:
Friction piles approach the uppermost layer of soft soil differently.
Instead of digging down to the rock layer, the idea of friction piles is an interchange of forces with the soil around the column, getting the benefit of the column’s surface area.
Pier Foundation:
The pier foundation is an underground cylindrical structural member that supports heavy loads of structures that cannot resist shallow foundations.
Unlike pile foundation, this types of foundation in construction can only transfer loads by bearing.
It is narrower than the pile foundation.
Types of Pier Foundation:
- Drilled Pier Foundation.
- Block Pier Foundation.
- Steel Pier Foundation.
- Concrete Pier Foundation.
- Concrete Block Pier Foundation.
- Brick Pier Foundation.
Caisson Foundation:
A Caisson foundation is most frequently used when constructing a bridge, pier, or other structure over water, but it may also be utilized to support highway overpasses, hillside residences, and other structures.
It is possible to float prefabricated caissons to the drilling site and place them in a dredging pit.
Caissons can be made on-site using a rebar mesh grid filled with concrete.
The loose ground is augured out until bedrock is reached in order to build a caisson foundation.
To avoid the earth or sand from caving in on the excavation, a hollow steel casing can be implanted.
Concrete is then poured from the bottom up, forcing any remaining groundwater out the top, and the reinforcing mesh rebar is then centred within the casing.
The casing can be replaced once the concrete has been sufficiently filled.
Types of Caisson Foundation:
The good foundation has several varieties as follows:
1. Open caissons:
A box with no bottom that is buried into the ground and supported using ballast weights and a muck tube to collect excess groundwater.
Work can be done inside the pressurized chamber.
2. Pneumatic caissons:
When maintenance work is required deep below or underwater, these caissons are designed to allow personnel to descend the shaft.
3. Monolithic caissons:
Monolithic caissons are large single-column reinforced concrete caissons.
4. Sump caissons:
Sump caissons are capable of pumping water from below.
Offshore oil drillers frequently utilize it to recirculate tainted water.
5. Box caissons:
After immersion in water, a hollow concrete box at the bottom and sides is filled with concrete.
In its hollow state, the box is less dense than water and it can float, but once it is filled it becomes stronger.
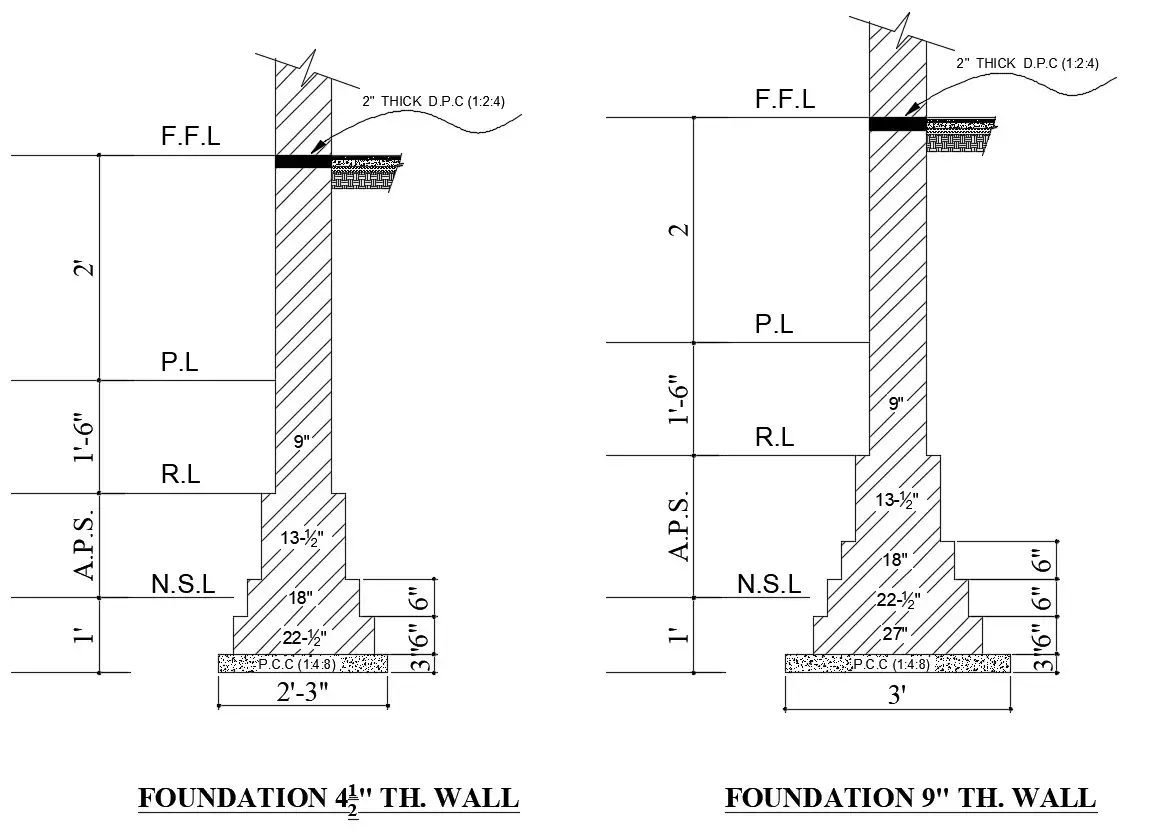
7. Shallow Foundation:
A shallow foundation is often broader than it is deep, they are sometimes known as spread foundations or open footings.
For valid reasons, shallow foundations are less expensive than the other type.
They are the most common because they do not require much soil drilling or digging.
Small foundations are beneficial when the structure is not too heavy and the earth can support a large amount of weight at such a shallow depth.
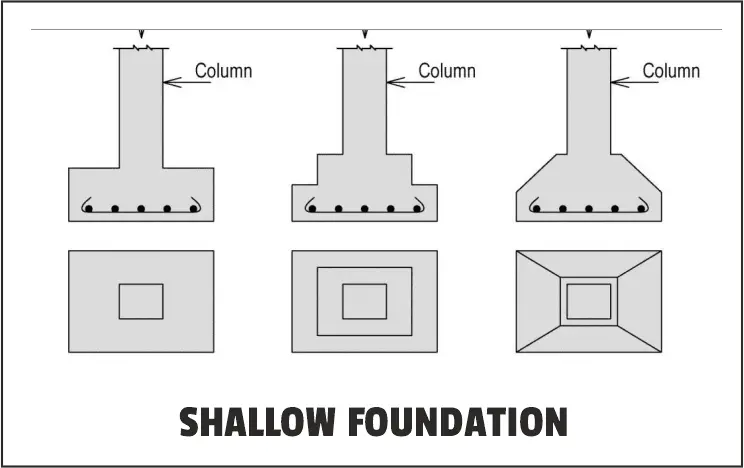
Types of Shallow Foundation:
There are four different types of shallow foundations, as follows: mat, individual footing, combination footing, and stem wall.
Each type of foundation has a different appearance and a variety of application cases.
1. Mat Foundation:
A mat foundation uses the whole surface area where the structure will be placed as the load-bearing foundation.
They are frequently utilized when the soil is loose and weak, or where the weight must be distributed uniformly.
This types of foundation in building construction is also used when a basement is feasible and the pillars or columns are spaced closely together.
Since it is buried in the ground like the hull of a raft in a body of water, the basement foundation is frequently referred to as a “raft foundation.”
2. Individual Footing:
Individual footings are one of the most prevalent types of shallow foundation.
Spread footings that support a particular column or pillar are frequently square, rectangular, or even geometric concrete blocks.
A footing is known as a wall, strip or continuous footing that runs the entire length of a load-bearing wall.
3. Combined Footing:
A combined footing is identical to an individual footing with the exception that one base bear the weight of two pillars or columns that are near enough to constitute a common foundation.
4. Stem Wall Foundation:
A foundation that extends the full length of a load-bearing wall is known as a wall, strip, or continuous footing.
Usually, strip footings are twice or three times the width of the reinforced concrete wall.
These type of foundations are employed when load-bearing walls, rather than columns, pillars, or beams, support the structure’s weight.
Strip foundations are typically used to construct masonry walls, but they may also be utilized well when constructing on gravel or closely packed sand.
Also read: Difference between Footing and Foundation
Types of Foundations in Building- Frequently Asked Questions:
A shallow foundation and deep foundation are generally two types of foundation in construction for building houses, and home structures.
Strip Footing.
Isolated or Spread Footing.
Combined Footing.
Cantilever or Strap Footing.
Mat or Raft Foundation.
Pile foundation.
Pier Foundation.
Caissons Foundation.
Shallow foundation and Deep foundation.
Concrete pile foundation.
Stone pile foundation.
Screw piles foundation.
Auger pile foundation.
Drilled pile foundation.
Pin pile foundation.
Bridge pile foundation.
Deep pile foundation.
Micropile foundation.
Mini pile foundation.
Conclusion:
All types of foundations in construction distribute the load of the structure over the large bearing area so that the intensity of loads is reduced within the safe bearing capacity of the soil.
Depending on the size, location, and geotechnical restrictions of your project, the shallow foundation or deep foundation may be understandable, but a specific type of foundation might be harder to identify.
The significance of the foundation types in a building construction to its overall structural stability, making the appropriate choice.





thank you very good
Awesome explanation thank you
Thanks very much ,,,have gained alot from it
Thank you for sharing.
Thank you for sharing..
Thanks a lot, this is indeed helpful.