A frost wall is a structure that rises above the frost line and serves as insulation for the ground around a building’s foundation.
In freezing climates, frost walls or frost-protected walls are constructed to keep the ground under buildings from freezing and protect their foundations.
In this article you’ll learn:
So, if you’re ready to go with it, this article is for you.
Let’s dive right in.
What is Frost Wall?
A frost wall is a protected wall constructed around the foundation’s edge built underground, below the frost line.
Since the frost wall is buried under the soil, the frost heave process won’t use any upward pressure on the foundation.
In the interior of a building structure, walls that are constructed above ground level can also be referred to as frost walls.
As a result, this will serve as insulation and keep the building’s interior warm.
Additionally, these frost walls retain heat from the building, avoiding soil freezing and other issues.
Purpose of Frost Wall:
- A frost-protected wall’s main function is to prevent the surrounding soil from freezing during extremely cold weather.
- Ice melts into the water at any temperature decrease, hence freezing and thawing process is necessary.
- These ice lenses will exert significant pressure on the nearby soil mixture.
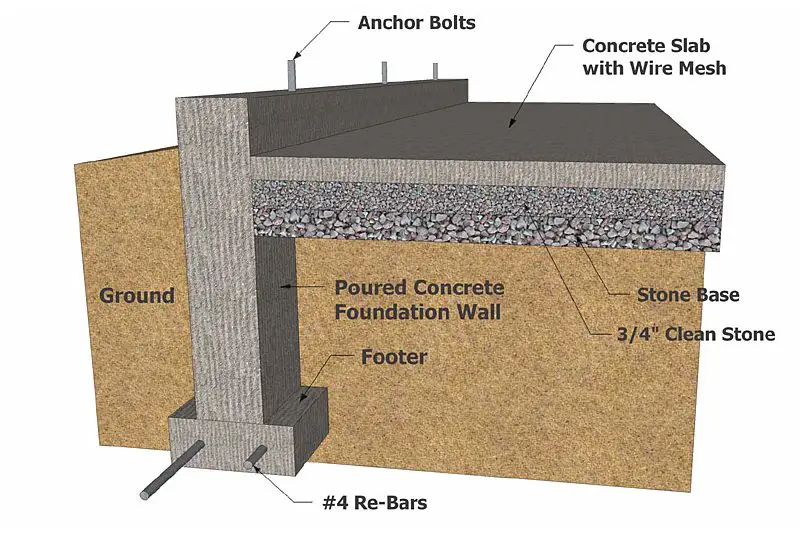
Types of Frost Walls:
Depending on the requirements of the load, temperature, and building features, various frost walls can be constructed as follows:
1. Frost Wall with Load Bearing:
The foundation will now be responsible for the frost wall due to its construction.
By being built beneath a substantial layer of soil, this wall will serve as a foundation wall.
This will be obviously built below the local frost line.
Extreme weather conditions are used to construct these frost walls (freezing temperatures).
2. Frost walls with Non-load Bearing:
These walls are built like an insulating wall.
There is no insulation in these built-in homes, these insulated non-load-bearing walls will be constructed inside the structure.
Non-load-bearing frost walls help to stop heat loss through the foundation, it is prohibited for the interior frost wall to touch the exterior wall.
While building the same, extra care should be taken.
A gap has been left between the two walls in order to prevent moisture from turning into ice inside the wall structure, it is also advised to have a barrier.
Requirements for Constructing the Frost Walls:
If all the structural components with this construction possess the necessary qualities, the construction of the frost wall performs better.
Some of the fundamental behaviors related to its requirements include the following:
- To avoid any gaps, the basement wall that was built under the wall needs to be patched.
- These basement walls are typically built using cinder blocks, the gaps can be filled with brick fillers.
- If the basement walls are made of concrete, it is necessary to use a paint sealer to fill in any cracks.
- There are specialized paints in the market that can aid in preventing moisture from entering the basement.
- All structural elements must be built with the main objective of preventing moisture invasion.
Advantages of Frost Wall:
- The building’s foundation allows heat to escape, preventing the ground below from freezing and heaving.
- An FPSF installation enables soil beneath the foundation to stay above freezing even during extremely cold winters when used in conjunction with geothermal heat storage.
Disadvantages of Frost Wall:
- In colder climates, frost damage to building structures is a serious problem.
- The construction is only influenced by the temperature properties of the building materials used.
Applications of Frost Walls:
1. Frost Wall for Shallow Foundation Protection:
Non-bearing frost walls are built with the purpose of defending a shallow foundation.
This type is used when building a frost wall as a deep foundation is either totally unfeasible for the area or doesn’t offer any kind of economic benefit.
Here, this wall is constructed by leaving a particular space between the foundation and wall as per the builder’s advice.
This is set up to prevent the soil from losing heat from it.
In order to effectively warm up the heat radiated from the building; such construction are built around the foundation.
On the both foundation’s exterior (vertically) and basement (horizontally), a rigid foam of insulation is built.
Since of the way these insulations are built, heat generated inside the building’s interior is transferred to the ground, keeping the soil from freezing.
2. Frost Wall for Non-Heated Buildings:
This wall will only warm the building if the structure being built is a heated structure, an non-heated building cannot be used.
A solution for this problem would be to design a horizontal layer that would be positioned beneath the building’s entire foundation.
This horizontal layer must also go beyond the boundaries of the building, vertical insulation of any kind is not offered.
Over the layer of gravel, the provided insulation is placed.
The warmth will be retained in the soil as a result, preventing it from freezing.
Also read: Masonry Wall | Load Bearing Wall | CMU Walls | Partition Wall | Cavity Wall
Conclusion:
These frost walls regularly absorb heat from their structure to keep the building’s underlying soil from freezing and other related conditions.
In the interior of a building system, walls are constructed above ground is referred as frost walls.
As a result, this will act as insulation to maintain the home’s interior temperature.

Related Posts
Rock Quality Designation(RQD): Building Strong Foundations
Spread Footing
Masonry Cement
Plain Cement Concrete
Concrete Efflorescence
Concrete Pile
Stepped Footing
Fineness Modulus of Coarse Aggregates
Difference between Condo and Apartment