There are several different types of concrete generally used for construction purposes, while concrete is made of cement, water, and coarse aggregates, when mixed together forms a building material that hardens over time.
The essential property in every concrete is that it sets and hardens to make a rock-like mass in a short period of time, ultimate strength and other properties of concrete depend on several factors such as:
- Nature of aggregate materials used.
- Cement quality and proportion of cement aggregates.
- Water used to make a mixture.
- Workmanship.
The composition is usually expressed as the relative volume of cement, fine aggregates (sand), and coarse aggregates (gravel, etc.), thus 1: 2: 4 represents 1 part of concrete, 2 parts of sand, and 4 parts of gravel or crush aggregate
In the actual mixture, the respective volumes are converted to the weight of the respective materials.
Different Types of Concrete and thier uses:
1.Normal Strength Concrete:
This normal strength concrete combines all the basic ingredients such as concrete, sand and aggregates using a 1: 2: 4 ratio, this general strength produces concrete.
It takes about 30 to 90 minutes to install but is dependent on weather conditions on the concrete site and cement properties commonly used for pavements or buildings that do not require high tensile strength.
This is not recommended for many other structures because it does not withstand the stresses created by wind loads or vibrations.
2.Plain or Ordinary Concrete:
This ordinary concrete also uses a common mixture design of 1: 2: 4 with components of cement, sand, and aggregates mainly used to built sidewalks or buildings, where there is not a high demand for tensile strength.
It faces challenges such as general strength concrete does not withstand vibration of air loading very well.
Plain or simple concrete is also used in dam construction, while the durability of such concrete is very satisfactory.
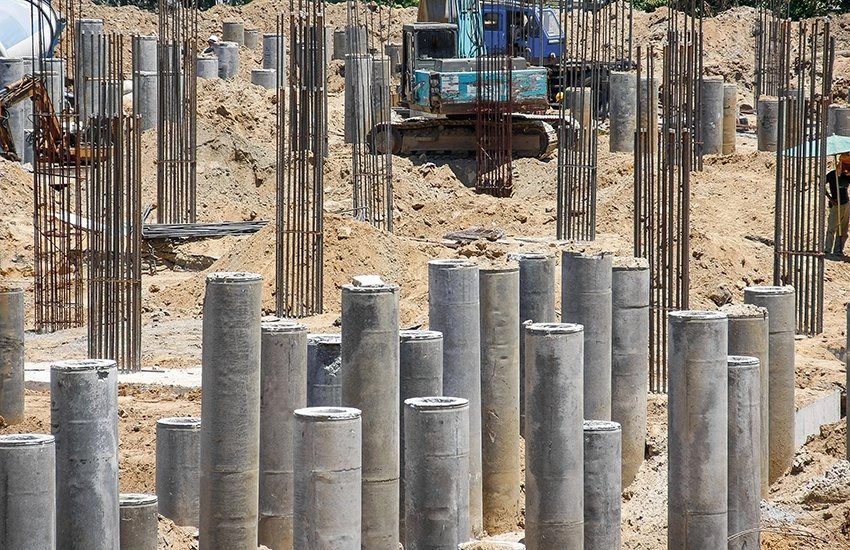
3.Reinforced Concrete:
This reinforced concrete is widely used in industry and modern construction, the strength of reinforced concrete is aided by placing wires, steel rods, or cables into the concrete before it set.
These reinforcements resist tensile forces while concrete itself helps to resist compressive forces, form a strong bond and two materials resist many applied forces.
In short, they become a single structural element built in the 19th century dramatically changed the construction industry, buildings, bridges, and roadways depend on reinforced concrete.
When you travel near a construction site, you are likely to see reinforced cement concrete with rebars.
4.Prestressed Concrete:
Many large concrete projects uses prestressed concrete units which is made using a special technique.
Like reinforced concrete, it includes bars or tendons but these straps or tendons are stressed before the actual application of concrete.
This types of concrete is mixed and placed, these bars are placed at each end of the structural unit where they are used.
When the solid is set, this unit is put into compression, this process makes the lower part of the unit stronger against tensile forces, however, requires heavy equipment and skilled labor.
Typically, prestressed units are built and assembled on-site as they are used to construct bridges, heavily filled structures, or roofs with long spans.
5.Precast Concrete:
This precast concrete is cast in a factory according to exact specifications, the concrete units are then transported to the location and assembled, it is used for concrete blocks, precast walls, stair items, and poles.
The benefit of using these types of concrete is its quick assembly as the units are manufactured in a factory and they are of very high quality.
6.Lightweight Concrete:
Lightweight concrete is the type of concrete whose density is less than 1920kg / m3, which is made using lightweight aggregates that add to the density of the concrete.
These lightweight aggregates include natural materials such as scoria or pumice, artificial materials such as clay and expanded shells, or processed materials such as vermiculite and perlite.
These concrete uses include building long spanning bridge decks and building blocks and to protect steel structures.
7.High-Density Concrete:
This high-density concrete has a very specific purpose in the construction of nuclear power plants, crushed rocks are commonly used.
Barytes, a colorless or white material containing barium sulfate and a major component in barium are the most frequently employed rock.
8.Air-Entrained Concrete:
This air-entrained concrete holds billions of microscopic air cells in every cubic foot, small air pockets relieve internal pressure on the concrete.
They provide small chambers where water can diffuse when it accumulates.
During the mixing process, the air is entered into the concrete by adding various foaming agents such as alcohol, resins, or fatty acids under careful engineering supervision as the concrete is mixed at the job site.
The entrained air adds up to about 3% to 6% of the volume of concrete, almost all types of concrete is used in cold environments or where there are freeze-melt cycles.
9.Ready-Mix Concrete:
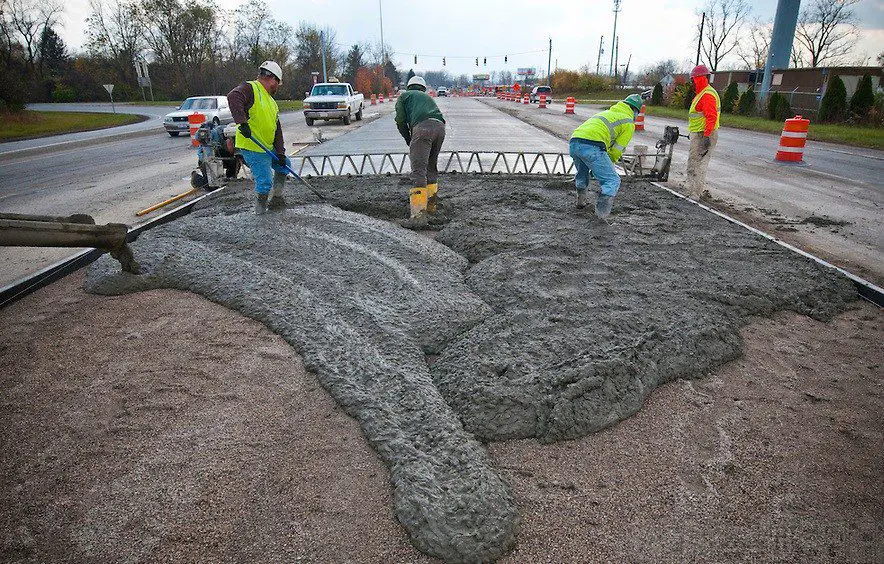
Concrete prepared and bathed in a centrally located plant is known as ready mixed concrete, this concrete is mixed and transported to the site in cement trucks often seen on roads and highways.
Once the truck arrives at the workplace, the cement can be used immediately as it does not require further treatment as it is a special concrete that is mixed based on developed specifications with great precision.
Forming ready-mix concrete requires a centralized location where concrete can be prepared, while these locations should be kept at an adjustable distance from the workplace.
If concrete takes too long to reach the workplace, it will be of no use.
In most cases, the workplace are away with the preparation plant, retired agents are sometimes used to find out how long concrete takes to set.
Ready-mix concrete is preferred over concrete mixing site because the mixture has high precision and minimizes confusion at the workplace for preparing concrete.
This concrete can be used for buildings, roadways, walls and more.
10.Volumetric Concrete:
This volumetric concrete is made an alternative for ready-mix concrete to solve the long-distance problem between the concrete plant and construction sites.
This requires special trucks called volumetric mobile mixers, they carry concrete material and water that will be mixed at the construction site.
Volumetric concrete is extremely useful when a builder needs to mix two different types of concrete at the same site and it is very useful on large sites, basement construction, and multi-projects.
11.Decorative Concrete:
This decorative concrete are visually and aesthetically creates concrete mixes.
Decorative concrete can undergo several processes, such as coloring, molding, polishing, etching and decorative topping.
It is ideal for any project in which you want to make an aesthetic statement, it adds a little decoration to dull surfaces or structures.
For example, swimming pools and floors can make great use of decorative concrete.
12.Rapid-Set Concrete:
This rapid set concrete is ideal when you are a short time to complete a project because it has a fast set time and very resistant to low temperatures, so it can be used at any time of the year.
This is especially useful in winter when the cold weather does not allow you to use many other types of concrete.
13.Smart Concrete:
This smart concrete provides a different method for monitoring the condition of reinforced concrete structures.
Small carbon fiber is added to the concrete using a conventional concrete mixer, this affects the electrical resistance of concrete when it encounters stress or strain.
This concrete is used to detect potential problems before concrete failure, it is very good at understanding small structural defects.
Smart concrete allows engineers to examine the health of structures after an earthquake which provides a far better assessment of their condition than visual inspection.
14.Pervious Concrete:
Pervious Concrete is one of the most common concrete used for road and pavement construction designed to deal with stormwater runoff, pool, and water problems on roadways or airport runways.
Roadways that use extensive concrete have fewer problems with hydroplaning, tire spray, and snow buildup, it also reducing the need to stop and storm sewer.
This concrete is made of a mixture of cement, water, and coarse aggregates which allows water to pass easily through the layers.
Some types of deformed concrete several gallons of water per minute pass through its surface.
15.Pumped Concrete:
Pumped concrete is very practical, and so it can be easily transported to the upper floor through pipes hence effective used on the upper floors of a very tall building,
This pipe will be a flexible or rigid hose that discharges the concrete to the required area.
16.LimeCrete:
Limecrete uses lime instead of concrete cement with light aggregates such as glass fiber or sharp sand mainly used for building floors, vaults, and domes.
It has many environmental benefits because it is easy to clean and renewable used with radiant floor heating.
17.Roll Compacted Concrete:
Roller Compacted Concrete is a familiar sight on many US highways enclosing a layer of concrete.
This concrete is a strong, dense concrete used on high-traffic highways with large vehicles, it emits fewer emissions during the concrete production process which benefits the environment.
It is used in road construction, airport runways, car parks, sidewalks and industrial servicing.
18.Glass Concrete:
Glass concrete is modern form of concrete which uses the recycled glass.
This concrete is used when an aesthetic appeal is an important element in the design of concrete.
This concrete commonly used in large-format slabs found on floors or decorative facades, it may contain shining or colored glass during the mixing process to give specific splashes of color or sparkle.
19.Asphalt Concrete:
The asphalt or blacktop are types of concrete that is often used on streets, airport runways, highways, etc.
Asphalt concrete is a dark mineral made from a mixture of hydrocarbons called bitumen.
The automobile business grew therefore need for asphalt is also increased and it is identified for its sturdiness, practicality, skid resistance, stability, fatigue resistance, flexibility, and permeability.
It is a mixture of aggregates and asphalt, while various mixtures of asphalt are used for different purposes.
20.Shotcrete:
The shotcrete is applied through a nozzle on a frame or formwork, since this application requires high pressure, the condensation process takes place at the same time.
Shotcrete is used to repair damaged wood, concrete or steel structures.
It is also commonly used when access to a work area is difficult or when the formwork is impractical or cost-prohibitive.
21.Stamped Concrete:
This stamped concrete has some minor differences mostly used for architectural purposes.
A stamp of various shapes and designs placed on concrete structures to achieve an attractive-looking design when they are in plastic state.
Pigment is used for coloring purposes.
22.Vacuum Concrete:
In this vacuum concrete, a considerable amount of water is poured into the concrete mixture and the mixture is poured into the formwork.
The excess water is then extracted from the concrete with the help of a vacuum pump, therefore it is known as vacuum concrete.
This technique is used to quickly obtain the strength of concrete, so it will achieve compressive strength within a period of 10 days compared to 28 days of normal concrete.
23.Permeable Concrete:
This permeable concrete is prepared in such a way that water can be poured into it, they have about 15 to 20% voids so that water can pass through them.
They are used in areas where hurricane issues persist.
24.Self-Consolidated Concrete:
This self consolidated concrete is compressed by its own weight, which means the process of consolidation.
There is no need to use a vibrator or manual condensation.
Practicality of this type of concrete is always high hence it is known as flowing concrete.
25.Fiber Reinforced Concrete (FRC):
Fibre reinforced concrete consists of steel fibers that are 10 to 20 microns in diameter and 10 to 50 mm in size, it enhances ductility, tensile strength, and several properties.
Fibers might be various materials such as metal, polymers, glass, carbon or even natural fibers such as coconut fiber.
Some varieties of fibers react with cement, special care have to be taken when using them.
This types of concrete are used mostly in overlay for sidewalks in bridges, airports, and industrial floors.
26.Fly Ash Concrete:
In this fly ash concrete, fly ash is used to make concrete obtained from coals.
Flyash can be used to exchange fine aggregates or cement or partially both as it improves sturdiness in fresh concrete, sturdiness and strength in hardened concrete.
The particles of fly ash are finer than the cement particles.
27.High Strength Concrete:
The concrete with strength better than 40 N / mm2 is called high-performance concrete (HPC).
High performance concrete is used to achieve properties such as high strength, low shrinkage, self-condensation, high fire resistance, etc.
Generally, the strength should be greater than 60 N / mm2.
28.Silica Fume Concrete:
In this silica fume concrete, silica fume is used, while silica fume is by-product of silica.
Normal concrete with a normal water-cement ratio always has fine holes that limit the strength of regular concrete.
Silica fume has very fine particles, therefore if it is added to the concrete mixture to reduce minute pore locations, resulting in high strength concrete.
Silica fume is also a pozzolana that will contribute to strength, thus silica fume with superplastic is an essential component of high-performance concrete and high strength concrete.
29.Polymer Concrete:
Polymerization is the process of converting monomers into polymers.
In normal concrete, you may have noticed that microscopic holes cannot be avoided.
The impregnation of the monomer in these pores and subsequent polymerization is a recently developed technique to reduce the porosity of concrete and improve its strength and other properties, it is called polymer concrete.
30.Ferrocement:
Ferrocement consists of staggered wire-mesh with a rich mixture of cement mortar.
Typically, steel wires with diameters of 0.5 to 1.0 mm are made into a mesh.
Mortar 1: 2 to 1: 3 is cast in formwork with fabricated steel in layers of wire mesh with a water-cement ratio of 0.4 to 0.45.
The steel content of this concrete will be as high as 300 to 500 kg/m3 of mortar since the material contains a large percentage of steel, it has high ductility and tensile.
31.Pre-packaged concrete:
Typically, this types of concrete is prepared by mixing various materials.
However, it is possible to pack some ingredients (coarse aggregates) into the formwork then fill the holes with specially prepared cement-sand grout so that it can fill all the holes and form a solid mass.
Pre-packed concrete is used in special situations such as large amounts of concrete having to be leveled without construction joints.
Also read: Types of Sand, Types of Cement & Types of Mortar
Conclusion:
Among all types of concrete, standard ready-mixed concrete are the most commonly used concrete, it is prepared for delivery to a concrete plant rather than mixed at the construction site, which guarantees the quality of the concrete.





Thanks very informative about concrete