WBM stands for water-bound macadam which is the most commonly used road construction procedure since 190 years, the broken stones of the base and surface course are bound by stone dust in the presence of moisture is called WBM road.
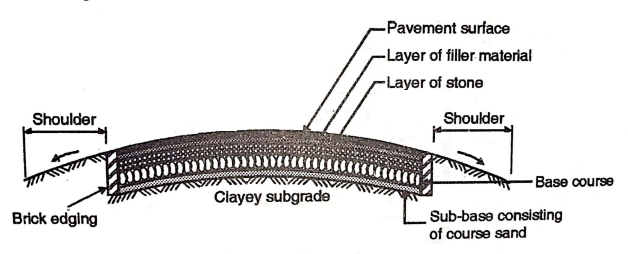
The road has its own wearing surface consisting of a clean, crushed aggregate which is mechanically rolled, bound together with filler material (screening), and the water laid on the finished base course.
Wearing surface is shaped by cleaned, crushed aggregates that are spread and rolled by sprinkling water.
The pavement base course made of crushed or broken aggregates interlocked by rolling and voids filled with water-assisted screening and binding materials.
Material Required for WBM Road:
1. Course aggregates:
Coarse aggregates that are commonly used in WBM road construction include crushed aggregates or broken stones for each layer of construction must be accepted as one of three gradings.
It used in the construction of WBM roads should be
- Durable, hard.
- Free from flaky and elongated particles.
- Acceptable shape.
- IRC has specified the physical requirements of coarse aggregation for WBM road construction over the period of test values of the three pavement layers.
2. Screenings:
Screening materials are usually small-sized aggregates of the same material as the course aggregates.
To reduce the cost of WBM road construction, the IRC recommends the use of non-plastic materials such as kankar nodules, murum or gravel.
Such material satisfies the following requirements as follows:
- The liquid limit is less than 20%.
- The plasticity index is less than 6%.
- The portion of fines passing 0.075 mm size sieve is less than 10%.
3. Binding Material:
The binding material used for WBM road construction should include an engineer-approved suitable material with a plasticity index value of less than 6.
It may not be necessary when the screening used is a crushable type, i.e. murum or gravel.
Construction of WBM Road:
1. Preparation of foundation for receiving the WBM course:
Subgrade or base courses are prepared for the required grades and camber, while depressions and pot-holes are filled on the existing road surface.
The corrugations are eliminated by scarifying and reshaping the surface to the required grade and camber as essential.
If the WBM road is to be supplied on the existing surface, the furrows of depth 50 mm and width 50 mm are minimized at intervals of 1 meter and at the center of the carriageway at 45 degrees earlier than laying the coarse aggregate.
2. Provision of Lateral Confinement:
To provide lateral confinement of the aggregates, a shoulder with a thickness equal to the compacted WBM layer must be constructed in advance.
Good earth or murum can be used in the construction of shoulders, they are prepared and rolled to maintain the road structure between them.
The practice of building WBM in the bench section excavated in the finished formation should be completely discouraged.
3. Spreading of Course Aggregates:
Aggregates that are stored along the road are then spread evenly and uniformly on the required amount of prepared base.
The number of layers and the total thickness of the WBM road will depend on the details of the design of the pavement as follows:
- For ordinary roads, a layer of compact thickness 75 mm is sufficient.
- For critical roads, two layers of equivalent 150 mm compact thickness may be provided.
- If a grading number set is used, it is compacted to a thickness of 100 mm.
4. Rolling:
After the aggregates are dispersed, rolling is carried out for compaction with the help of a three-wheel power roller of 6 to 10 tons capacity or an equivalent vibratory roller.
The rolling process is an efficient operation depends on the proper completion of the WBM road surface.
The roller should pass evenly over the entire surface and its speed should be slow and uniform, it should start from the side of the road and carry it up to the crown.
Each successive strip must overlap the preceding strip to avoid the formation of weak points.
The effect of defective rolling as follows:
- There is the formation of corrugations on a road surface.
- There is the unequal finish of road surface.
- The road starts wearing out very fast at places where the metal is not properly deposited.
On the super-elevated section of the wbm road, rolling starts from the inner or lower edge and moves slowly towards the outer or upper edges of the pavement.
5. Application of screenings:
After the compaction of course aggregates, screening is applied to fill the interstices.
Screening is applied in three or more layers, while each layer is compacted by dry rolling.
Screening has to be spread evenly, the rolling and sweeping of each layer of screening must be done carefully.
6. Sprinkling and Grouting:
After the application of screening, the wbm road surface is sprayed with plenty of water then swept and rolled.
Hand sweep is used to clean wet screening in the wedge.
Additional screening is applied and rolled until the coarse aggregates are well bonded and set firmly.
7. Application of Binding Material:
The binding material is then applied at a uniform and slow rate in two or more layers.
After each application of binding material, the surface is sprayed with plenty of water, and wet slurry is used to fill with hand rooms or mechanical rooms then rolled with a 6 to 10-ton roller.
During rolling, water is applied to the wheel of the rollers to wash the binding material that is stocked on the surface of the roller.
8. Setting and Drying:
The wbm road surface is allowed to cure or set in the night after final rolling.
If depressions are found the next day, they are filled with screening or binding material, if necessary water is sprayed and the surface is rolled.
9. Preparation of shoulder:
During curing, the shoulders are prepared by filling the earth at the specified cross slope.
These are then correctly compacted by rolling or tamping.
10. Opening to traffic:
After drying, the street is opened to traffic.
Traffic should be well distributed over the entire width of the road by placing long obstacles in the form of drums, tree branches, etc. on the road surface.
Advantages of WBM Road:
- The cracks are not formed on the surface of bituminous roads.
- Maintenance costs are low.
- The surface of these roads is non-slippery.
- Such roads are waterproof roads.
- It provides a smooth, durable and comfortable road surface for traffic.
- Such roads eliminate dust infiltration.
- It can resist the adverse effects of rain, changes in temperature, and wind flow.
- The cost of construction is low.
- No skilled laborers are required.
- Made from locally available material.
- If maintained in good condition, it can carry a traffic load of about 900 tons per lane per day.
Disadvantages of WBM Road:
- Life is short.
- If the WBM road surface is poorly maintained, it causes inconvenience and hazard to the traffic.
- These types of roads are sometimes permeable to rainwater and lead to softening and yield of subsoil.
- If the bituminous material exceeds the optimal value for a given mixture, it proves detrimental to the good performance of the bituminous road.
- The viscosity of the bitumen aggregate mixture plays an excellent role in determining the efficiency of bituminous roads.
Also read: Road Drainage, Town Planning & Road Pattern
Conclusion:
As the population is increasing day-to-day, we have to enhance our WBM road for higher effectiveness in transportation by keeping in mind the future aspects to full fill the requirements of road users.
All environmental impacts, vehicle characteristics, human characteristics must be taken into consideration.

Related Posts
Refresh Your Office: Simple Ideas to Boost Productivity and Motivation in Your Workplace:
Understanding the Nuances of Office Chair Vs Ergonomic Chair to Select Better!
Rock Quality Designation(RQD): Building Strong Foundations
Spread Footing
Masonry Cement
Plain Cement Concrete
Concrete Efflorescence
Concrete Pile
Stepped Footing