In building construction, the shear wall is rigid vertical diaphragms capable of transferring lateral forces from the outer walls, floors, and ceilings to the ground level in the parallel direction of their planes i.e. reinforced-concrete walls or vertical trusses.
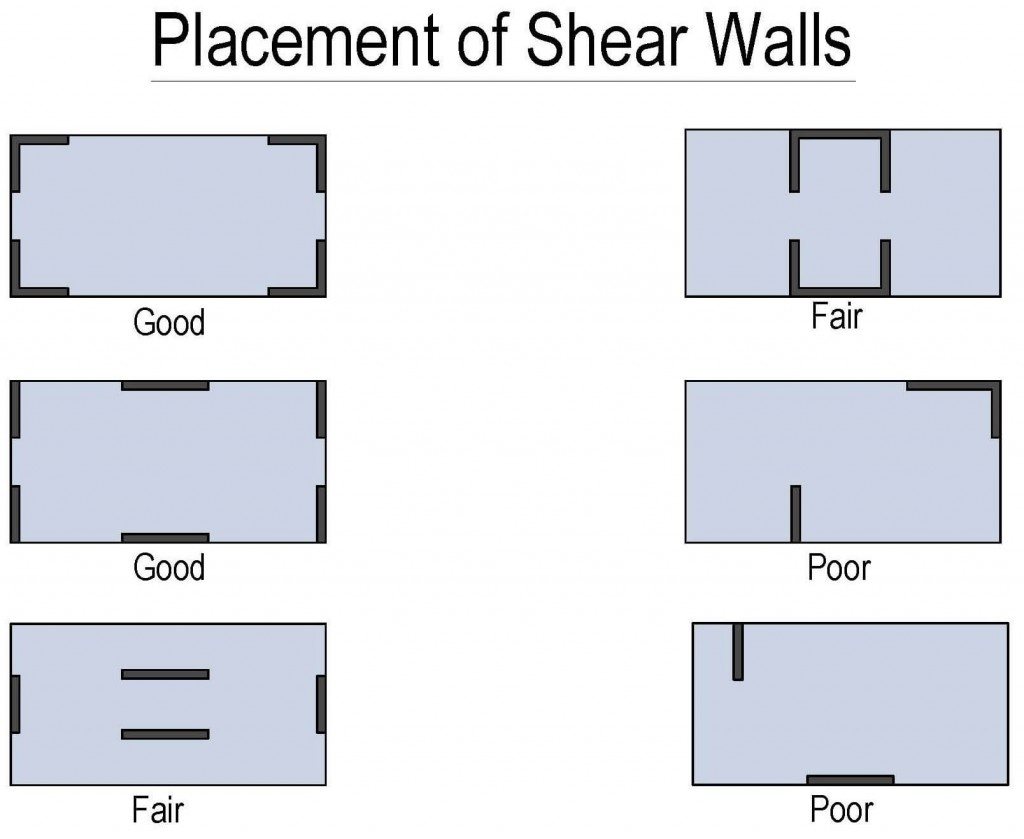
The behavior of these walls depends on the material used, the wall thickness, length & position of the wall in the building frame.
We will learn about the shear wall, types of the shear wall, why and where the shear wall is provided!
Introduction to Shear Wall:
A shear wall is a structural component provided to the multistoried or tall buildings or ordinary buildings in high wind velocity areas.
These walls usually begin from the foundation level, along the length and width of buildings.
Their thickness can be above 150 mm or below 400 mm in tall buildings and they are like vertical-oriented wide beams that carry the earthquake load towards the foundation.
Why and where shear wall is provided:
- This wall resists the lateral loads that are imposed on the structure due to wind, earthquake, or sometimes due to hydrostatic or lateral earth pressure.
- Shear wall buildings are a common choice in earthquake-prone countries.
- They are efficient in reducing construction costs.
- Also reduces earthquake damage in structural and non-structural elements such as glass windows and construction materials.
- Buildings with shear walls have shown very good performance during earthquakes in high seismic areas.
Types of Shear Wall:
1. RC Shear Wall:
RC wall consists of reinforced concrete walls and reinforced concrete slabs.
Their wall thicknesses range from 140 mm to 500 mm, depending on construction age and thermal insulation requirements.
Usually, these walls stay at the height of the entire building; however, some walls are closed to the road front or basement level to permit industrial or parking areas.
Sometimes, the wall structure is symmetric with respect to at least one axis within the plan.
Usually, wall reinforcement consists of two layers of reinforcements distributed through the length of the wall.
Also, vertical reinforcement bars are offered near the door and window openings on the wall end zones.
2. Plywood Shear Wall:
Plywood is the standard materials used within the building of shear walls.
The development of prefabricated shear panels has made these walls reinforce small shear assemblies falling on both aspects of the opening.
Using sheet steel and steel-backed sheer panels at the structural location has proven sturdy in seismic resistance.
3. MIDPLY Shear Wall:
The MIDPLY shear walls are improved wood shear walls developed to redesign joints between the sheathing and framing members.
The modes of failure observed in normal wall testing cause lateral load levels to trigger failures in normal walls.
Within the MIDPLY shear walls design, a ply of shielding materials is positioned within the centre of the walls between a series of pairs of studs oriented in a 90° rotated position relative to standard shear walls.
4. RC Hollow Concrete Block Masonry Walls:
These walls are constructed by reinforcing hollow concrete block masonry in hollow locations.
It requires steady metal rods in vertical and horizontal directions at structurally dynamic places of wall panels, full of fresh grout concrete in hollow locations of masonry blocks.
Their elements are designed as load-bearing walls for gravity loads and earthquake loads to safely resist earthquakes.
5. Steel Plate Shear Wall:
Usually, the steel plate shear walls system consists of steel plate walls, boundary column, and horizontal backside beam collectively with the steel plate walls and boundary column acting as a vertical plate girder.
The columns act as flanges of the vertical plate girder and the steel plate wall serves as its web.
Horizontal backside beams act, roughly as transverse strainers in a plate girder.
Materials used for shear wall construction:
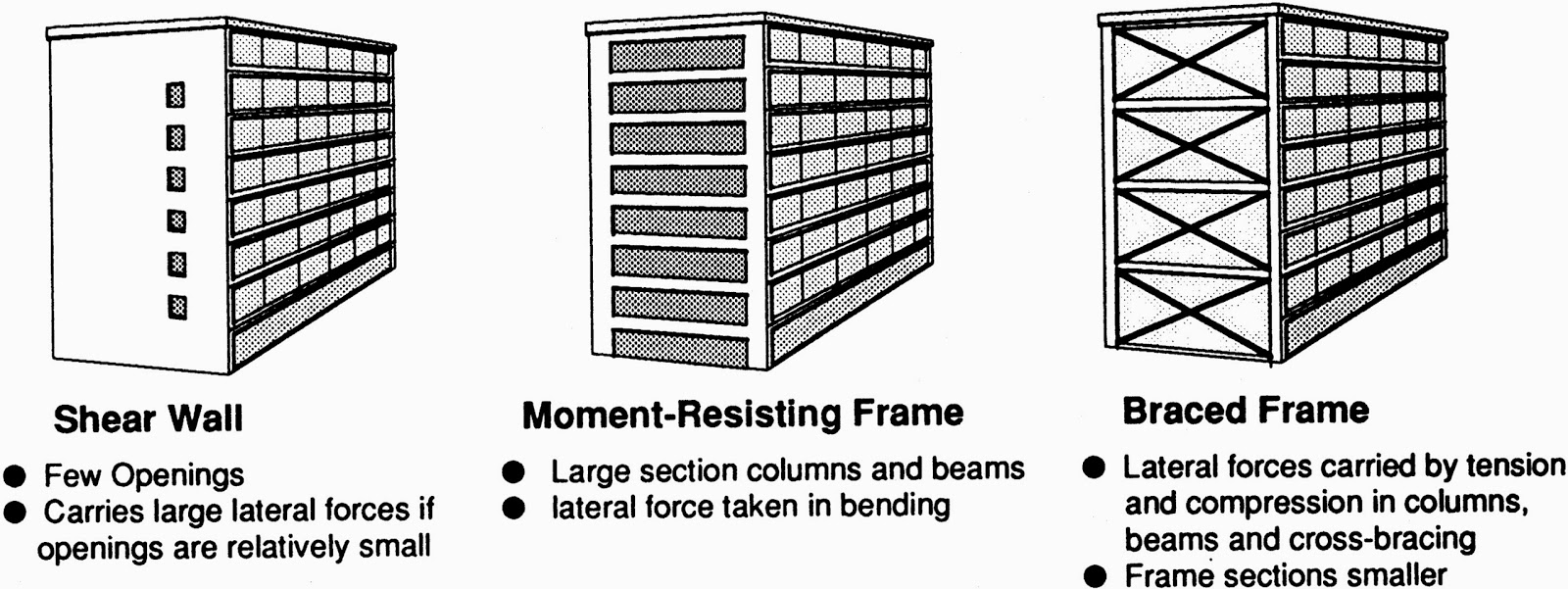
This wall usually is designed as a braced moment-resisting frame usually made of structural steel or the reinforced concrete wall.
Though it may also be made using plywood or masonry structure.
The Braced Frame (steel) used as a shear walls.
Moment Resisting Frame (steel) used as a shear walls.
The Continuous rigid structures with few openings, either made of reinforced concrete or masonry are used as shear walls.
Also read: Load Bearing Wall, Curtain Wall & Masonry Wall
Advantages of shear wall:
- Shear walls provide large strength and stiffness in the direction of orientation.
- It considerably reduces the lateral sway.
- They are easy in construction and implementation.
- It is efficient in terms of construction cost and minimizing earthquake damage.
- Also, provides strength and rigidity in the direction of alignment.
- These walls minimize the damages to structural and non-structural elements.
- They have enough well-distributed reinforcements.
- Also, requires less construction time.
- These walls are thinner walls.
- They are also lightweight.
Also read: Partition Wall, CMU Walls & Cavity Wall
Disadvantages of shear wall:
- Shear walls are difficult to construct.
- They have a flimsy appearance.
- Also, loud banging sounds associated with the buckling of web plates.
- It has low stiffness and energy dissipation capacity.
- Also, requires large moment connections.
Also read: Gabion Wall, Retaining Wall & Parapet Wall
Application of Shear Wall:
- Shear walls are designed to resist gravity / vertical loads and earthquake/wind lateral loads.
- These types of walls are structurally combined with the roof or the floor.
- Other lateral walls run at right angles to provide three-dimensional stability to structures.
- The walls have to resist uplift forces due to air drag.
- These walls resist the shear forces that try to push the walls up and the lateral forces of air that push the walls in and out of the structure.
- This shear walls structural system is extra stable.
- The supporting area is comparatively high compared to RCC framed structures.
Frequently Asked Questions:
The shear wall protects the house or building from being deformed by horizontal (lateral) pressures during heavy winds, hurricanes, or earthquakes.
The load-bearing walls maintain the structure upright by transmitting the structure’s compression load to its base, while the shear wall prevents the structure from falling by resisting lateral wind forces and seismic pressures.
Wall thickness varies from 40 mm to 500 mm.
Conclusion:
Shear wall is the most effective building element that resists lateral forces during an earthquake, high wind damage and minimize the effects of lateral forces caused by an earthquake.
The construction of these walls will give the buildings too much stiffness which will damage the structure.
For accommodation of a large number of populations in the small area structures, shear walls are considered most useful.
In the developing country, the shear walls are backbone of the construction industry.





Hi Rahul,
Very nice article. Since Shearwalls is all concrete, my assumption is the R-value is less and it will let heat and cold easily through the walls. What ae some efficient ways to insulate internal walls to reduce heat coming to the building and requiring large amount of Air Con in tropical climate like south india.
Dear Sir/Madam
hope you fine and doing well.
Its is my first times use from web its helpful Information for me.
More Success,
Imran Khan Ibrahimi.